From: RFID Made Easy Date: 2025-10-23
Selecting the right RFID Antenna is one of the most important decisions when designing an RFID system. The antenna directly influences read range, accuracy, and data reliability, all critical to achieving consistent system performance. Because every deployment environment and use case is unique, choosing the right antenna requires a careful, data-driven approach. Below are five key considerations from the RFID experts at Argo Wireless to guide your selection.
Key Considerations for Antenna Selection:
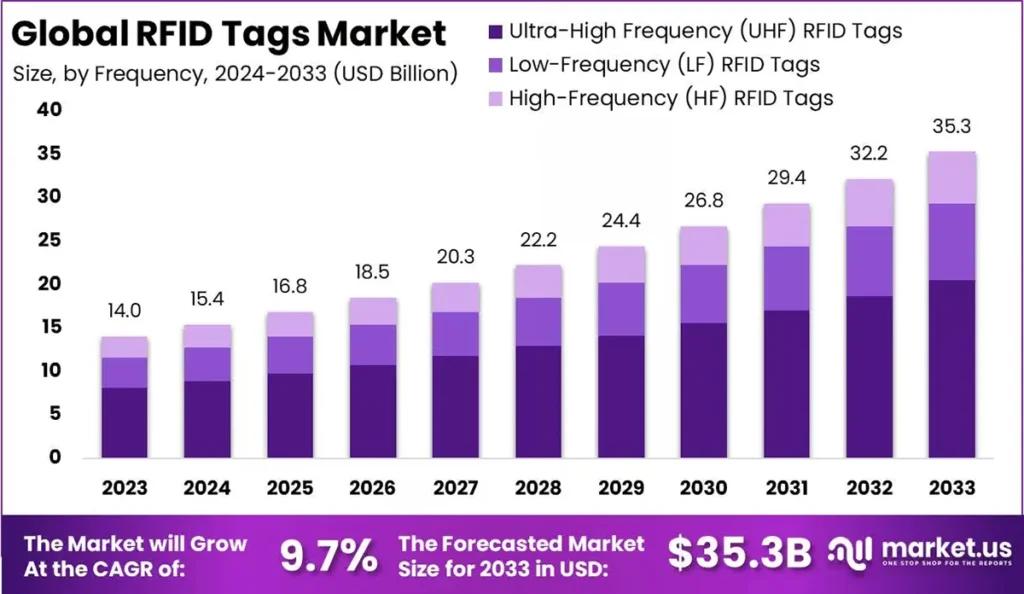
1. Frequency Range: Most RFID systems today rely on UHF (Ultra High Frequency) technology, which represents more than 60% of the global RFID market. UHF RFID delivers longer read ranges, faster data transfer, and lower tag costs than LF (Low Frequency) or HF (High Frequency) systems. UHF RFID is widely used in logistics, retail, manufacturing, and industrial automation, especially as more AI-driven systems depend on real-time data from RFID tags for decision-making and predictive insights.
2. Operating Environment: Your environment determines the type of antenna you need. Outdoor or industrial deployments require ruggedized designs built to withstand moisture, dust, and temperature extremes. Look for antennas with at least an IP67 rating for water and dust protection.
Determine whether the antenna will be used indoors or outdoors. Harsh environments require rugged designs that can withstand dust, water, and temperature extremes. Look for antennas rated IP67 or higher for durability.
3. Performance and Range: Performance varies by application. High-gain antennas are preferred for large warehouses, yards, or manufacturing lines that need extended read distances and narrow beam patterns.
4. Physical Form Factor: Installation constraints and mounting options play a major role in antenna selection. Some environments call for low-profile or ultra-thin antennas, especially in retail or smart shelf applications where space is limited. The physical space and mounting requirements are important.
5. Specific Use Case: Every RFID application demands a tailored approach. Antennas can be optimized for wide-beam indoor coverage, long-range outdoor tracking, or specialized zones like conveyor belts and dock doors. Different antennas are designed to match the needs of common use cases.
RFID Expert Guidance
Selecting the right RFID antenna involves more than comparing specs, it’s about aligning antenna capabilities with your system’s environmental and operational demands. Analyze your environment and select the optimal antennas, cables, and readers to ensure your deployment succeeds.